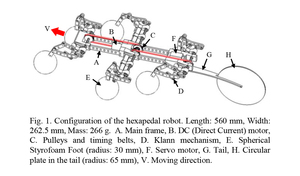
Steering control of a water-running robot using an active tail
2016
Conference Paper
pi
Many highly dynamic novel mobile robots have been developed being inspired by animals. In this study, we are inspired by a basilisk lizard's ability to run and steer on water surface for a hexapedal robot. The robot has an active tail with a circular plate, which the robot rotates to steer on water. We dynamically modeled the platform and conducted simulations and experiments on steering locomotion with a bang-bang controller. The robot can steer on water by rotating the tail, and the controlled steering locomotion is stable. The dynamic modelling approximates the robot's steering locomotion and the trends of the simulations and experiments are similar, although there are errors between the desired and actual angles. The robot's maneuverability on water can be improved through further research.
| Author(s): | Kim, HyunGyu and Jeong, Kyungmin and Sitti, Metin and Seo, TaeWon |
| Book Title: | Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on |
| Pages: | 4945--4950 |
| Year: | 2016 |
| Month: | October |
| Day: | 9 |
| Department(s): | Physical Intelligence |
| Bibtex Type: | Conference Paper (inproceedings) |
| DOI: | 10.1109/IROS.2016.7759726 |
| Organization: | IEEE |
|
BibTex @inproceedings{kim2016steering,
title = {Steering control of a water-running robot using an active tail},
author = {Kim, HyunGyu and Jeong, Kyungmin and Sitti, Metin and Seo, TaeWon},
booktitle = {Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on},
pages = {4945--4950},
organization = {IEEE},
month = oct,
year = {2016},
doi = {10.1109/IROS.2016.7759726},
month_numeric = {10}
}
|
|