Integrating mechanism synthesis and topological optimization technique for stiffness-oriented design of a three degrees-of-freedom flexure-based parallel mechanism
2015
Article
pi
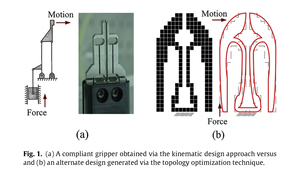
This paper introduces a new design approach to synthesize multiple degrees-of-freedom (DOF) flexure-based parallel mechanism (FPM). Termed as an integrated design approach, it is a systematic design methodology, which integrates both classical mechanism synthesis and modern topology optimization technique, to deliver an optimized multi-DOF FPM. This design approach is separated into two levels. At sub-chain level, a novel topology optimization technique, which uses the classical linkage mechanisms as DNA seeds, is used to synthesize the compliant joints or limbs. At configuration level, the optimal compliant joints are used to form the parallel limbs of the multi-DOF FPM and another stage of optimization was conducted to determine the optimal space distribution between these compliant joints so as to generate a multi-DOF FPM with optimized stiffness characteristic. In this paper, the design of a 3-DOF planar motion FPM was used to demonstrate the effectiveness and accuracy of this proposed design approach.
| Author(s): | Lum, Guo Zhan and Teo, Tat Joo and Yang, Guilin and Yeo, Song Huat and Sitti, Metin |
| Journal: | Precision Engineering |
| Volume: | 39 |
| Pages: | 125--133 |
| Year: | 2015 |
| Month: | January |
| Publisher: | Elsevier |
| Department(s): | Physical Intelligence |
| Bibtex Type: | Article (article) |
| DOI: | 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.07.012 |
|
BibTex @article{lum2015integrating,
title = {Integrating mechanism synthesis and topological optimization technique for stiffness-oriented design of a three degrees-of-freedom flexure-based parallel mechanism},
author = {Lum, Guo Zhan and Teo, Tat Joo and Yang, Guilin and Yeo, Song Huat and Sitti, Metin},
journal = {Precision Engineering},
volume = {39},
pages = {125--133},
publisher = {Elsevier},
month = jan,
year = {2015},
doi = {10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.07.012},
month_numeric = {1}
}
|
|