Clinical translation of wireless soft robotic medical devices
2024
Article
pi
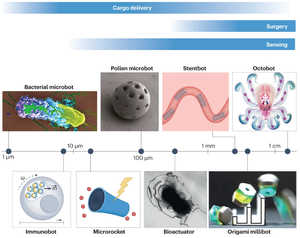
Small-scale wireless soft robotics can be designed as implantable, interventional or wearable devices for various biomedical applications. Their flexibility, dexterity, adaptability and safe interactions with biological environments make them promising candidates for enabling precise and remote healthcare and disease diagnosis. However, the clinical translation of wireless soft robotic medical devices remains challenging. In this Review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the robotic technologies, the navigation methods, the dexterous functions and the translational challenges of wireless soft robotic medical devices. We first discuss safety and biocompatibility from a biological and technical perspective and then examine navigation methods for overcoming biological barriers for delivery, mobility and retrieval, highlighting dexterous medical functions at small scales. Finally, we identify key product development challenges, as well as the regulatory and ethical considerations that should be addressed to enable the clinical translation of wireless soft robotic medical devices.
| Author(s): | Wang, Tianlu and Wu, Yingdan and Yildiz, Erdost and Kanyas, Selin and Sitti, Metin |
| Journal: | Nature Reviews Bioengineering |
| Year: | 2024 |
| Department(s): | Physical Intelligence |
| Bibtex Type: | Article (article) |
| Paper Type: | Journal |
| DOI: | https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-024-00156-7 |
|
BibTex @article{wang2024clinical,
title = {Clinical translation of wireless soft robotic medical devices},
author = {Wang, Tianlu and Wu, Yingdan and Yildiz, Erdost and Kanyas, Selin and Sitti, Metin},
journal = {Nature Reviews Bioengineering},
year = {2024},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-024-00156-7}
}
|
|